State of Border and Movements within Southern Africa
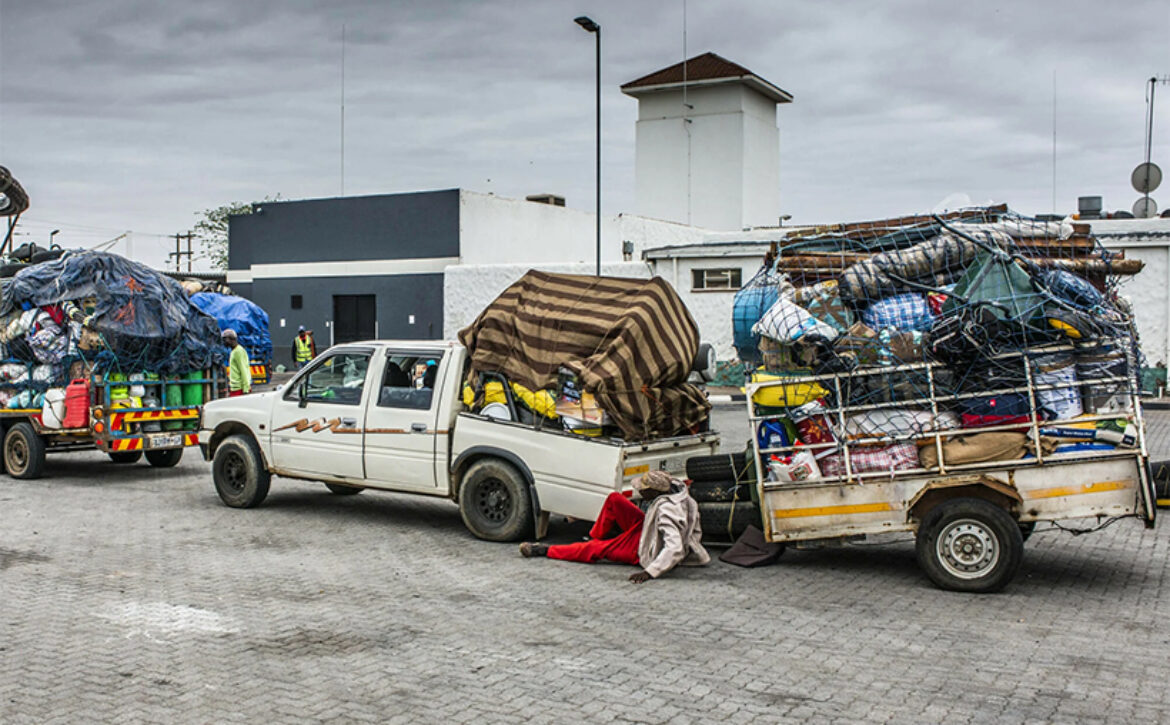

Overview of the State of Border Management in Southern Africa
Introduction and Background
At the core of border management systems of nation states is the desire to balance two seemingly contrasting goals: preventing and reducing cross-border security threats on one hand and the facilitation of movement of goods and people for improved trade on the other (African Union, 2020; International Organisation for Migration, 2017). Border management thus encompasses the intersection of mobility and security interests (International Organisation for Migration, 2017).
In recent years, security issues in southern Africa have included terrorism and extremism (as currently happening in northern parts of Mozambique); transnational crimes such as human trafficking, drug peddling, cattle rustling, among others. Thus, achieving a good balance between the security and mobility goals depends on effective border management policies and practices within the key areas of identity management, border management information systems, integrated border management and humanitarian border management, and thus significantly contributing to achievement of several targets within the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as goal 10, target 10.7 (migration and mobility), and several targets in goals 9 (resilient infrastructure, inclusive industrialisation and innovation) , 16 (peaceful and inclusive societies) and 17 ( revitalising global partnerships) just to mention a few (International Organisation for Migration, 2017).